Understanding Colon Cancer Screening
2022-11-21
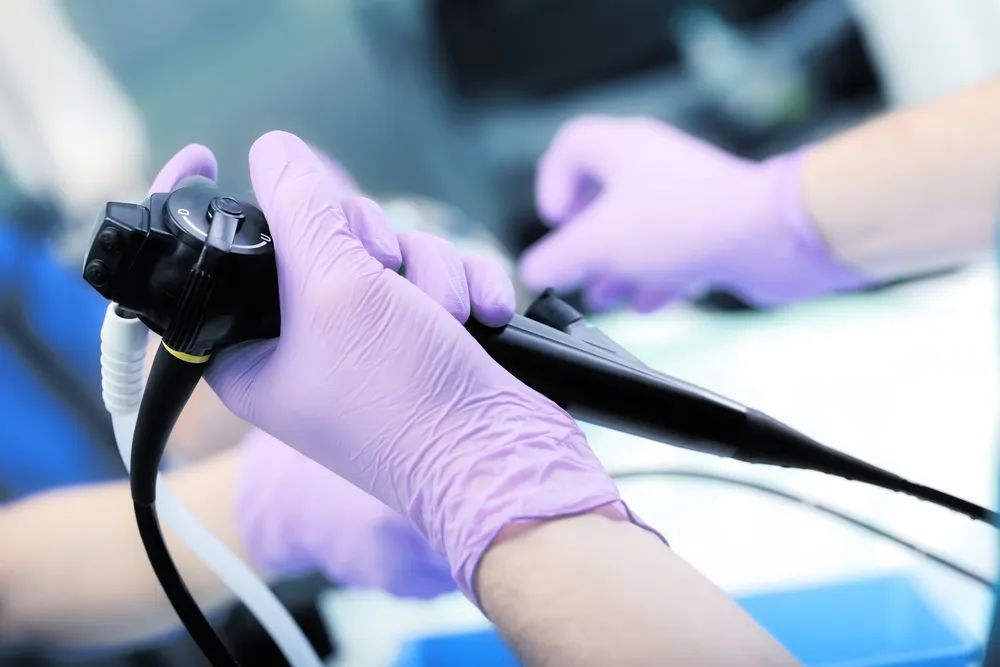
PARKWAY 百汇医疗 Six Questions That Could Save Your Life (or the Life of Someone You Love) Test your knowledge about colorectal cancer (CRC) screening. If you think the answer is true or mostly true, answer true. If you think the answer is false or mostly false, answer false. NO.1 Colorectal cancer is predominantly a “man’s disease,” affecting many more men than women annually. FALSE. Colorectal cancer affects an equal number of men and women. Many women, however, think of CRC as a disease only affecting men and might be unaware of important information about screening and preventing colorectal cancer that could save their lives, says the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. NO.2 Only people over the age of 50 who are currently experiencing some symptoms or problems should be screened for colorectal cancer or polyps. FALSE. Beginning at age 50, all men and women should be screened for colorectal cancer EVEN IF THEY ARE EXPERIENCING NO PROBLEMS OR SYMPTOMS. In addition, African-American people and all people with a family history of colorectal cancer should be screened earlier. Discuss your individual risk factors with your doctor to determine the appropriate timing and type of your first screening and each screening thereafter. NO.3 A colonoscopy screening exam typically requires an overnight stay in a hospital. FALSE. A colonoscopy screening exam is almost always done on an outpatient basis. A mild sedative is usually given before the procedure and then a flexible, slender tube is inserted into the rectum to look inside the colon. The test is safe, and the procedure itself typically takes less than 45 minutes. NO.4 Tests used for screening for colon cancer include colonoscopy, fecal immunochemical (FIT) test, FIT-DNA or stool DNA test, FIT-fecal DNA, flexible sigmoidoscopy and CT colonography. TRUE. Once CRC has taken hold, there are symptoms. But screening tests can catch cancer in early stages before symptoms appear, or prevent cancer from developing altogether. Talk to your healthcare provider about which test is best for you. Current recommended screening options* include: Beginning at age 50, experts recommend the following as the best tests: A colonoscopy every 10 years (the most accurate and the only test that can remove precancerous polyps) OR A FIT (fecal immunochemical) test every year. A positive result on a FIT test requires follow-up with a colonoscopy. For those who can’t or won’t undergo these tests, other options include: CT colonography every 5 years FIT–fecal DNA test every 3 years Flexible sigmoidoscopy (recommended frequency varies from every 5 years to every 10 years) However, colonoscopy will be needed to follow up on positive results of these tests. *Important: You may need to begin periodic screening colonoscopy earlier than age 50 years if you have a personal or family history of colorectal cancer, polyps or long-standing ulcerative colitis. For people with certain risk factors, colonoscopy is the only appropriate screening test. NO.5 Colorectal cancer is often preventable. TRUE. Colorectal cancer is highly preventable. Colonoscopy may detect polyps (small growths on the lining of the colon). Removal of these polyps (by biopsy or snare polypectomy) results in a major reduction in the likelihood of developing colorectal cancer in the future. Tests other than colonoscopy are designed to detect cancer as opposed to pre-cancerous lesions that can be dealt with before they become a cancer. IMPORTANT REMINDER: This information is intended only to provide general guidance. It does not provide definitive medical advice. It is very important that you consult your doctor about your specific condition. Parkway China Parkway is part of IHH Healthcare, one of the largest healthcare providers in the world by market capitalization. Its operates 80 hospitals with more than 15,000 beds in 10 countries. Parkway first arrived in China in 2004. In 2006, Parkway opened its first medical center in Shanghai, bringing world-renowned quality healthcare to China. Through the acquisition of World Link Group in 2007, Parkway becomes Shanghai's largest foreign-owned medical network. Parkway China is a leading international healthcare provider. With a team of nearly 100 internationally trained physicians, we now operate 8 medical facilities conveniently located in Shanghai, Chengdu and Hong Kong offering more than 40 specialties. We work closely with the best local hospitals with which we share our knowledge and expertise to ensure the best services possible to our patients. We have established direct billing services with over 50 insurance companies. We provide both outpatient and inpatient care for adults and children. Our services include: Family Medicine, Adult Medicine, Pediatrics, Gynecology, Dentistry, Cardiology, ENT, Gastroenterology, Ophthalmology, Dermatology, General Surgery, Orthopedics & Sports Medicine, Urology, Beauty & Skin Care, Psychiatry, Traditional Chinese Medicine & Acupuncture, Osteopathy, etc.